PATHWAY 1 Get user input in an app: Part 1
1. Kotlin의 클래스 및 상속
클래스 계층 구조와 상속

- 속성, 동작이 비슷한 항목을 그룹(상위클래스)으로 분류하고 더 구체적인 유형의 카테고리(하위클래스)를 만들 수 있음.
- 상위 그룹의 속성을 모두 포함하거나 상속 받음
- 그룹에 속하더라도 각각의 고유한 속성이 있음
- 상속 : 하위 클래스가 상위 클래스의 모든 속성과 메서드를 포함하거나 물려받는 것. 상속을 통해 코드를 공유하고 재사용할 수 있음
추상 클래스
- 추상 클래스 : 추상 멤버(속성 혹은 메소드)를 하나 이상 포함하는 클래스
- 특징
- 클래스의 스케치
- 완전히 구현되지 않아 인스턴스화(객체화)할 수 없음
- 구체적인 세부 정보의 결정은 서브 클래스에게 맡김
- 사용하는 경우
- 모든 서브 클래스에 공통적인 속성과 함수를 포함시켜서 구조화할때 (클래스 그룹에 공통되지만 각 클래스 내에서 고유하게 구현되어야 하는 기능을 설명할 때)
- 속성값과 함수 구현을 알 수 없을 때
- 사용법 : 키워드 abstract
abstract class Dwelling(private var residents){ abstract val buildingMaterial:String abstract val capacity: Int //추상 멤버 선언시 타입 명시 필수 fun hasRoom() : Boolean { return capacity > residents } } - 추상 클래스의 서브 클래스 작성
class SquareCabin(residents: Int): Dwelling(residents) { override val buildingMaterial = "Wood" override val capacity = 6 }
서브 클래스 만들기
- Kotlin에서 기본 클래스는 최종클래스임 (type is final) -> 기본 클래스는 상속이 불가능하다.
- 클래스 상속을 하는 방법 (해당 클래스가 상위 클래스가 되려면)
- 추상 클래스일 경우
- open 키워드 사용
주택 계층 구조.Kt
import kotlin.math.PI
import kotlin.math.sqrt
fun main() {
val myCabin = SquareCabin(6, 50.0)
val myHut = RoundHut(3, 10.0)
val myTower = RoundTower(4, 15.5)
with(myCabin)
{
println("\nSquareCabin\n============")
println("Capacity : ${capacity}")
println("Material : ${buildingMaterial}")
println("hasRoom?: ${hasRoom()}")
println("Floor area: %.2f".format(floorArea()))
}
with(myHut)
{
println("\nRoundHut\n============")
println("Capacity : ${capacity}")
println("Material : ${buildingMaterial}")
println("hasRoom?: ${hasRoom()}")
getRoom()
println("hasRoom?: ${hasRoom()}")
getRoom()
println("Floor area: %.2f".format(floorArea()))
println("Carpet size : %.2f".format(calculateMaxCarpetSize()))
}
with(myTower)
{
println("\nRoundTower\n============")
println("Capacity : ${capacity}")
println("Material : ${buildingMaterial}")
println("hasRoom?: ${hasRoom()}")
println("Floor area: %.2f".format(floorArea()))
println("Carpet size : %.2f".format(calculateMaxCarpetSize()))
}
}
abstract class Dwelling(private var residents: Int){
abstract val buildingMaterial:String
abstract val capacity: Int
abstract fun floorArea():Double
fun getRoom()
{
if(hasRoom())
{
residents++
println("You got a room!")
}
else
{
println("Sorray, at capacity and no rooms left.")
}
}
fun hasRoom() : Boolean
{
return capacity > residents
}
}
class SquareCabin(residents: Int, val length: Double) :Dwelling(residents)
{
override val buildingMaterial = "Wood"
override val capacity = 6
override fun floorArea():Double
{
return length * length
}
}
open class RoundHut(residents: Int, val radius: Double): Dwelling(residents)
{
override val buildingMaterial = "Straw"
override val capacity = 4
override fun floorArea():Double
{
return radius * radius * kotlin.math.PI
}
fun calculateMaxCarpetSize(): Double
{
val diameter = 2 * radius
return sqrt(diameter * diameter /2)
}
}
class RoundTower(residents: Int, radius: Double, val floors: Int = 2):RoundHut(residents, radius)
{
override val buildingMaterial = "Stone"
override val capacity = 4 * floors
override fun floorArea():Double
{
return super.floorArea() * floors
}
}2. xml 레이아웃 만들기
사용할 UI 요소
- EditText : 텍스트 입력, 수정
- TextView : 텍스트 표시
- RadioButton : 라디오 그룹 내 버튼 여러개 중 하나 선택 가능한 라디오 버튼
- RadioGroup : 라디오 버튼들 그룹화
- Switch : 켜기/끄기 전환 버튼
XML
- eXtensible Markup Language
- 텍스트 기반 문서를 사용하여 데이터를 설명하는 방법
- Android 앱의 UI 레이아웃 정의 등 다양한 용도로 사용됨
- 태그, 요소, 속성으로 구성됨
문자열 추출
- 하드 코딩 문자열 관련 경고 → Extract String Resource
- 문자열 리소스 이름 : 기본이름 or 새로 지정
- 문자열이 그 값 그대로 사용하는 게 아니라 리소스로 따로 저장해두고 사용하는 것
- 유지, 보수할 때 유용함
<resources>
<string name="app_name">Tip Time</string>
<string name="cost_of_service">Cost of Service</string>
<string name="how_was_the_service">How was the service?</string>
<string name="amazing_20">Amazing (20%)</string>
<string name="ok_15">OK (15%)</string>
<string name="good_18">Good (18%)</string>
<string name="calculate">calculate</string>
<string name="tip_amount">Tip Amount: %s</string>
<string name="round_up_tip">Round up tip?</string>
</resources>activity_main.xml (팁계산기 레이아웃)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:padding="16dp"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<EditText
android:id="@+id/input_cost_of_service"
android:layout_width="180dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="@string/cost_of_service"
android:inputType="numberDecimal"
android:textSize="24sp"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txt_service_question"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/how_was_the_service"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/input_cost_of_service" />
<RadioGroup
android:id="@+id/tip_options"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:checkedButton="@id/option_twenty_percent"
android:orientation="vertical"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/txt_service_question">
<!--add RadioButtons here-->
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/option_twenty_percent"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/amazing_20" />
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/option_eighteen_percent"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/good_18" />
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/option_fifteen_percent"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/ok_15" />
</RadioGroup>
<Switch
android:id="@+id/switch_round_up"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:minHeight="48dp"
android:text="@string/round_up_tip"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/tip_options" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_calculate"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/calculate"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/switch_round_up" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txt_result"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@+id/btn_calculate"
tools:text="Tip Amount: $10" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>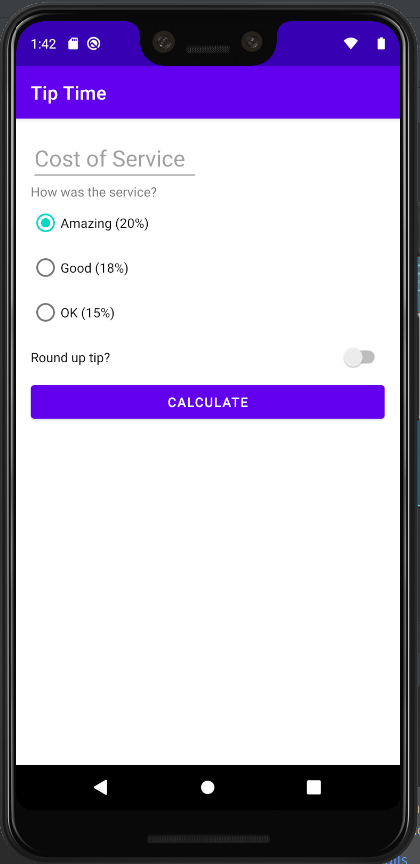
3. 팁 계산기 기능 구현
뷰 결합
- 코드가 UI 요소에 액세스하려면 findViewById()를 사용해서 ID를 통해 View에 대한 참조를 찾아서 접근
- 그러나 이방식은 UI가 복잡해지면 번거로운 작업이 될 수 있다.
- 대안 : 뷰 결합 - findViewById() 를 사용해서 ID를 통해 View에 대한 참조를 찾아서 접근
- 뷰 결합 사용 설정
- build.gradle 파일 열기 (Gradle Scripts > build.gradle (Module: Tip_Time.app))
- android 섹션에 다음 줄 추가
- Gradle files have changed since last project sync. 메시지 → Sync Now
- 이벤트 로그 창에 Gradle sync finished 메시지 표기되면 파일 닫기
buildFeatures { viewBinding = true }
findViewById vs view Binding
- findViewById() : 앱의 각 view 마다 호출
- view Binding
- 결합 객체 한번 만들고 초기화함.
- binding 객체는 ID가 있는 앱의 모든 View를 위한 참조를 자동으로 정의함.
- View를 위한 참조를 유지할 변수를 만들 필요 X , 결합 객체에서 직접 뷰 참조를 사용하면 됨
// Old way with findViewById()
val myButton: Button = findViewById(R.id.my_button)
myButton.text = "A button"
// Better way with view binding
val myButton: Button = binding.myButton
myButton.text = "A button"
// Best way with view binding and no extra variable
binding.myButton.text = "A button"
+) 결합 클래스의 이름
- (언더 바 제외 후) XML 파일의 이름을 카멜 표기법으로 변환
- 이름 끝에 'Binding'을 추가하여 생성됨
ex) activity_main.xml→ ActivityMainBinding
+) 뷰를 위한 참조 :
- 언더바 제외하기
- 카멜 표기법으로 변환 후 생성
ex) binding.textView : @id/text_view에 액세스, binding.calculateButton : @id/calculate_button 에 액세스
lateinit 키워드
- 변수를 실제로 사용하기 전에 먼저 초기화 할것임을 확인해줌
- 변수를 초기화 하지 않으면 앱이 비정상 종료됨
var binding: ActivityMainBinding
//오류 : Property must be initialized or be abstract
lateinit var binding: ActivityMainBinding
MainActivity.kt
package com.example.tiptime
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import android.os.Bundle
import com.example.tiptime.databinding.ActivityMainBinding
import java.text.NumberFormat
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
lateinit var binding: ActivityMainBinding
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
binding = ActivityMainBinding.inflate(layoutInflater)
setContentView(binding.root)
binding.btnCalculate.setOnClickListener{ calculateTip()}
}
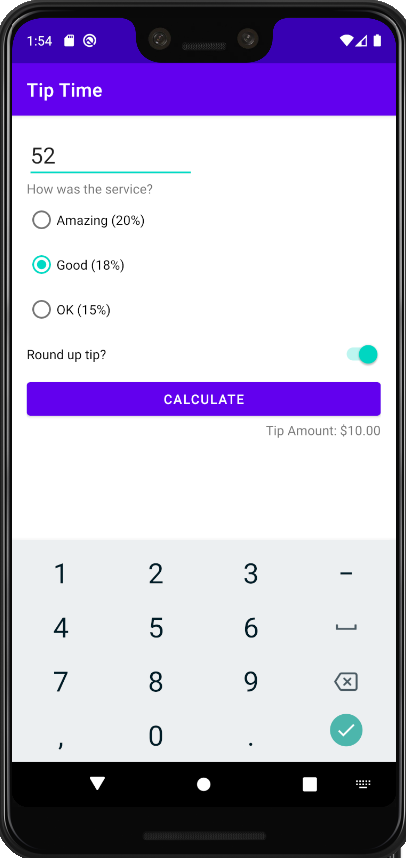
fun calculateTip()
{
//서비스 비용 가져오기
val stringInTextField = binding.inputCostOfService.text
val cost = stringInTextField.toString().toDouble()
//팁 비율 가져오기
val selectedId = binding.tipOptions.checkedRadioButtonId
val tipPercentage = when(selectedId)
{
R.id.option_twenty_percent -> 0.20
R.id.option_eighteen_percent -> 0.18
else -> 0.15
}
//팁 계산
var tip = cost * tipPercentage
//팁 반올림
val roundUp = binding.switchRoundUp.isChecked
if(roundUp)
{
tip = kotlin.math.ceil(tip)
}
//팁 표시하기
val formattedTip = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance().format(tip)
binding.txtResult.text = getString(R.string.tip_amount, formattedTip)
}
}
PATHWAY 2 Get user input in an app: Part 2
1. 앱 테마 변경
머터리얼 디자인
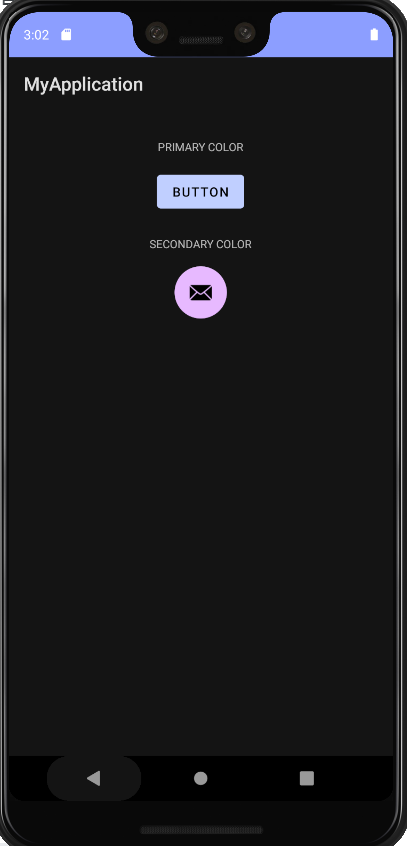
- 머티리얼 디자인 : 앱 UI를 빌드하는 방법에 관한 가이드라인 제시, 기본 테마 제공
- 머티리얼 테마 : 맞춤 설정으로 앱에 맞게 머티리얼 디자인 조정 가능
색상
- color.xml 파일에서 작은 색상 샘플 클릭 → 색상 선택 가능
- 머티리얼팀에서 제공하는 웹기반 색상 도구 : https://material.io/resources/color/#!/?view.left=0&view.right=0
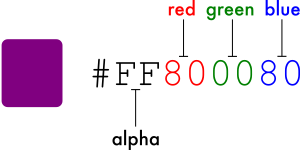
색상 - alpha
- 투명도
- #00 - #FF, 16진수 숫자
- 포함되지 않으면 #FF = 100% , 불투명
- RGB : 3개의 16진수 숫자로 구성
테마
- 스타일 : 글꼴 색상, 글꼴 크기, 배경 색상 등 View의 속성을 지정할 수 있다.
- 테마 : 개별 View뿐 아니라 앱, 활동 또는 뷰 계층 구조 전체에 적용되는 스타일의 모음
- 테마 색상
- -Variant : 해당 색상의 그림자
- colorOn- : 대비 (텍스트나 아이콘에 사용됨)
기본 테마 - themes.xml
- 앱 이름을 기반으로 하는 테마이름 : "Theme.MyApplication"
- 상위 속성 테마 : "Theme.MaterialComponents.DayNight.DarkActionBar"
- DayNight : 머티리얼 구성요소 라이브러리에 미리 정의된 테마
- DarkActionBar : 어두운 색상 사용
- 테마에 정의되지 않은 테마 색상 속성은 상위테마의 색상 사용
<style name="Theme.MyApplication" parent="Theme.MaterialComponents.DayNight.DarkActionBar">
<!-- Primary brand color. -->
<item name="colorPrimary">@color/purple_500</item>
<item name="colorPrimaryVariant">@color/purple_700</item>
<item name="colorOnPrimary">@color/white</item>
<!-- Secondary brand color. -->
<item name="colorSecondary">@color/teal_200</item>
<item name="colorSecondaryVariant">@color/teal_700</item>
<item name="colorOnSecondary">@color/black</item>
<!-- Status bar color. -->
<item name="android:statusBarColor" tools:targetApi="l">?attr/colorPrimaryVariant</item>
<!-- Customize your theme here. -->
</style>
색상 대비
- 텍스트를 사용할 때 명확하게 읽을 수 있는지
- 높을 수록 좋음
- 작은 텍스트 : 4.5:1 이상
- 큰 텍스트 : 3.0:1 이상
테마 색상 바꿔보기
- 색상에 관한 리소스 정의 (colors.xml)
- 파일에 색상 리소스 추가
<color name="green">#1B5E20</color>- themes.xml 에서 테마 색상 변경
- 테마 속성에 맞게 색상 변경하기
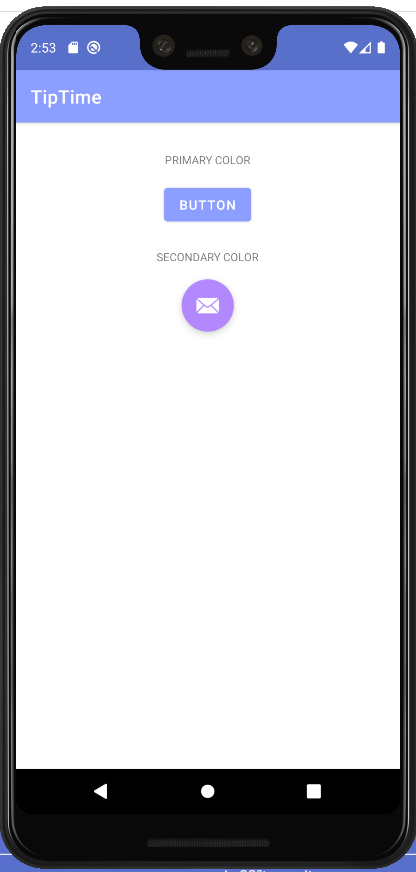
테마 색상 변경
어두운 테마
- themes.xml (night)(app > res > values > themes > themes.xml(night))
- colorPrimary -> (@color/green_light)(밝은 색상)
- 어두운 표면 색상(dark mode)에서 대비를 높이기 위해 밝은 색상 기본색상으로 사용
- colorPrimaryVariant -> @color/green
- colorSecondary-> @color/blue_light
- colorSecondaryVariant-> @color/blue_light
+) 애뮬레이터 실행 후 설정에서 야간모드로 변경하면 어두운 테마 적용된 것 확인 가능
+) Design Editor 에서 야간 모드 확인하는 법 : Orientation for Preview - night / not night
2. 앱 아이콘 변경
런처 아이콘
- 밀도 별로 앱 아이콘 리소스를 제공
- mdpi - 중밀도 화면의 리소스(~160dpi)
- hdpi - 고밀도 화면의 리소스 (~240dpi)
- xhdpi - 초고밀도 화면의 리소스(~320dpi)
- xxhdpi - 초초고밀도 화면의 리소스(~480dpi)
- xxxhdpi - 초초초고밀도 화면의 리소스(~640dpi)
- nodpi - 화면의 픽셀 밀도와 관계없이 조정할 수 없는 리소스
- anydpi - 어떤 밀도로도 조정 가능한 리소스
적응형 아이콘
- 백그라운드 레이어, 포그라운드 레이어 + 마스크 적용
- 벡터 이미지 : 한번 정의한 이미지로 어떤 화면 밀도에도 화질 저하 없이 캔버스 크기 조절 가능
앱 아이콘 변경
- 백그라운드, 포그라운드에 해당하는 벡터 드로어블 리소스 다운로드 (.xml 파일)

- 기존 앱 아이콘 리소스 삭제
- 다운받은 파일을 Image Asset으로 추가
- 기본 설정은 똑같이 두고 파일 위치를 찾아서 파일만 바꿔줌
- resize 기능을 통해 아이콘을 적절하게 사이즈 조정하기
3. 더욱 세련된 사용자 환경 만들기
머티리얼 디자인
- 앱에서 머티리얼 스타일을 더 쉽게 구현할 수 있는 UI 위젯
- 머티리얼 디자인 가이드 라인 : https://material.io/components/selection-controls#switches
Material Design
Build beautiful, usable products faster. Material Design is an adaptable system—backed by open-source code—that helps teams build high quality digital experiences.
material.io
- 머티리얼 아이콘 활용하기 : https://fonts.google.com/icons?selected=Material+Icons
- 스타일 및 테마 변경하기
사용자 환경 향상하기
- 기기 회전하시 UI 구성요소가 잘리는 버그 해결 : ConstraintLayout 주위에 ScrollView 추가
- Enter 키를 누르면 키보드 숨기기
- 음성 안내 지원을 사용하여 앱 테스트하기





댓글